Featured Snippet Answer
Too much biotin may cause acne, digestive discomfort, headaches, and inaccurate blood test results, especially thyroid-related tests.
Is Biotin Safe to Take Daily?
Biotin is generally considered safe for daily use because it is a water soluble vitamin. This means that excess amounts are usually filtered by the kidneys and excreted through urine rather than stored in the body.
For most healthy individuals, moderate supplementation does not cause problems. However, taking very high doses of biotin consistently may still lead to unwanted effects, particularly when doses exceed what the body needs for normal function.
Understanding proper dosage is important to avoid unnecessary risks.
Common Side Effects of High Biotin Intake
While many people tolerate biotin well, some may experience side effects, especially at higher doses. Commonly reported effects include:
- Acne or skin breakouts, particularly around the chin and jawline
- Mild nausea or stomach discomfort
- Headaches
- Changes in laboratory test results
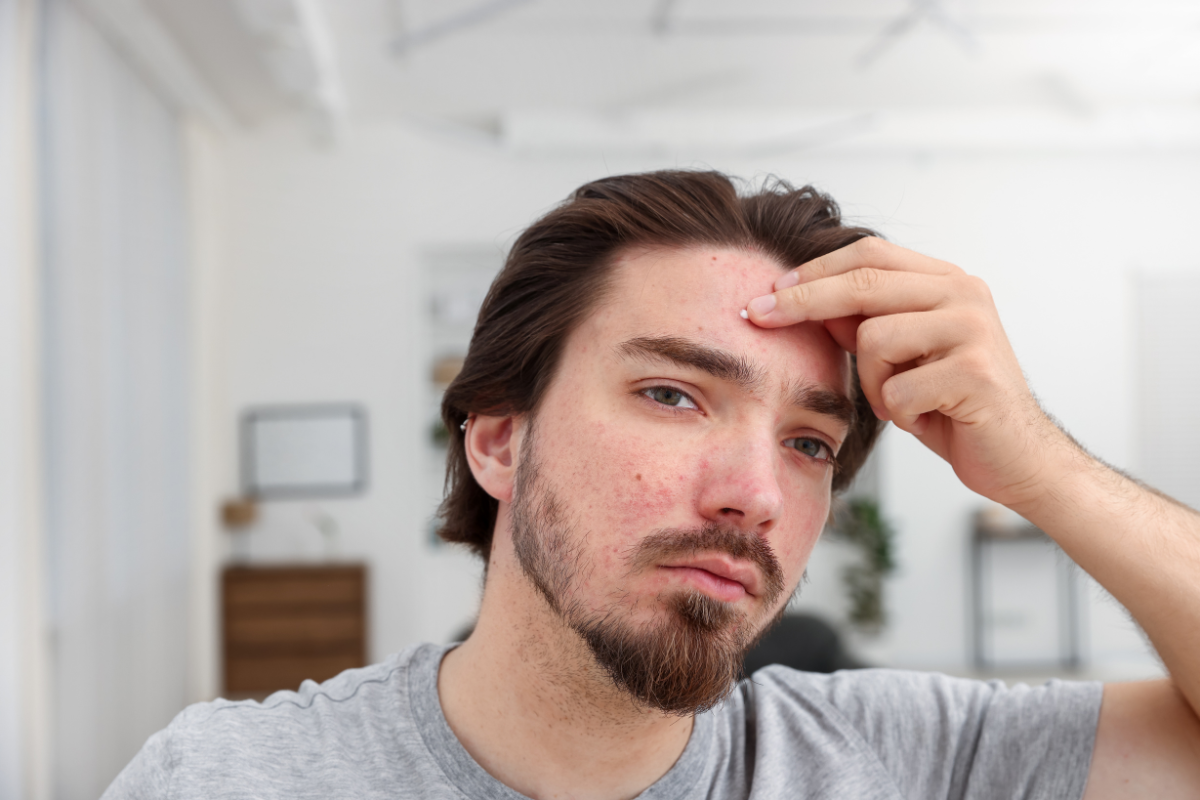

These side effects are more commonly reported when daily intake exceeds 10,000 micrograms.
Not everyone will experience these effects, but they are more likely with prolonged high-dose supplementation.
Why High Doses of Biotin Can Cause Skin Breakouts
One reason biotin may contribute to acne is its interaction with other B vitamins, particularly vitamin B5. High levels of biotin may interfere with the absorption of vitamin B5, which plays a role in maintaining healthy skin.
This imbalance may increase oil production in some individuals, leading to clogged pores and breakouts.
Biotin and Blood Test Interference
One of the most important safety concerns with high-dose biotin is its ability to interfere with certain blood tests.
High levels of biotin in the bloodstream can affect tests used to measure:
- Thyroid hormone levels
- Heart enzymes such as troponin
- Certain hormone markers
This interference can lead to falsely high or falsely low results, which may cause confusion or misdiagnosis if biotin use is not disclosed.
You can learn more about this topic in how long to stop biotin before blood tests.
How Long Do These Side Effects Last?
Most biotin-related side effects resolve once supplementation is reduced or stopped. Because biotin does not stay in the body long term, symptoms such as digestive discomfort or skin breakouts often improve within days to weeks.
Blood test interference may last longer, especially after high-dose use. This is explained in detail in how long does biotin stay in your system.
Who Should Be Extra Careful With Biotin?
You should consult a healthcare professional before taking high doses of biotin if you:
- Take high-dose biotin supplements daily
- Have thyroid conditions
- Undergo regular blood testing
- Take heart or blood pressure medication
These individuals may still be able to take biotin, but dosage and timing should be carefully managed.
How to Reduce the Risk of Biotin Side Effects
To minimize potential side effects:
- Avoid unnecessary high doses
- Do not stack multiple supplements containing biotin
- Inform healthcare providers about biotin use before blood tests
- Choose a dose appropriate for your needs
For guidance on proper intake, see how much biotin should you take daily.
When Should You Stop Taking Biotin?
If you experience persistent side effects or are scheduled for blood testing, it may be appropriate to temporarily stop biotin supplementation. Most people can resume use after testing unless advised otherwise by a healthcare provider.
Biotin is generally safe when used responsibly, but excessive intake may lead to unwanted side effects and lab test interference. Understanding appropriate dosage and knowing when to be cautious helps ensure safe and effective use.
For a complete overview of benefits, dosage, and safety considerations, visit biotin for hair growth.

